A blood pressure smartwatch is a new type of wearable device that combines the functions of traditional blood pressure monitors with those of a smart watch. It not only allows real-time monitoring of the user’s blood pressure but also features heart rate monitoring, sleep analysis, exercise tracking, and various health management functions. Through wireless connectivity, users can seamlessly sync monitoring data to their smartphones or cloud platforms for comprehensive data analysis and health management.

Working Principle of Blood Pressure Smartwatches
The working principle of blood pressure smartwatches primarily involves two methods: optical sensors and mechanical sensors.
1. Optical Sensor Method
– This method utilizes Photoplethysmography (PPG) technology, where an optical sensor on the smartwatch emits light that penetrates the skin.
– The sensor detects changes in the reflected light and analyzes blood flow dynamics to calculate pulse wave velocity changes.
– Advanced algorithms convert this pulse wave information into blood pressure values.
2. Mechanical Sensor Method
– Some smartwatches use built-in micro air bladders and pressure sensors to replicate the cuff inflation and deflation process of traditional blood pressure monitors.
– By detecting pressure changes and the transit time of pulse waves, accurate blood pressure readings can be obtained.
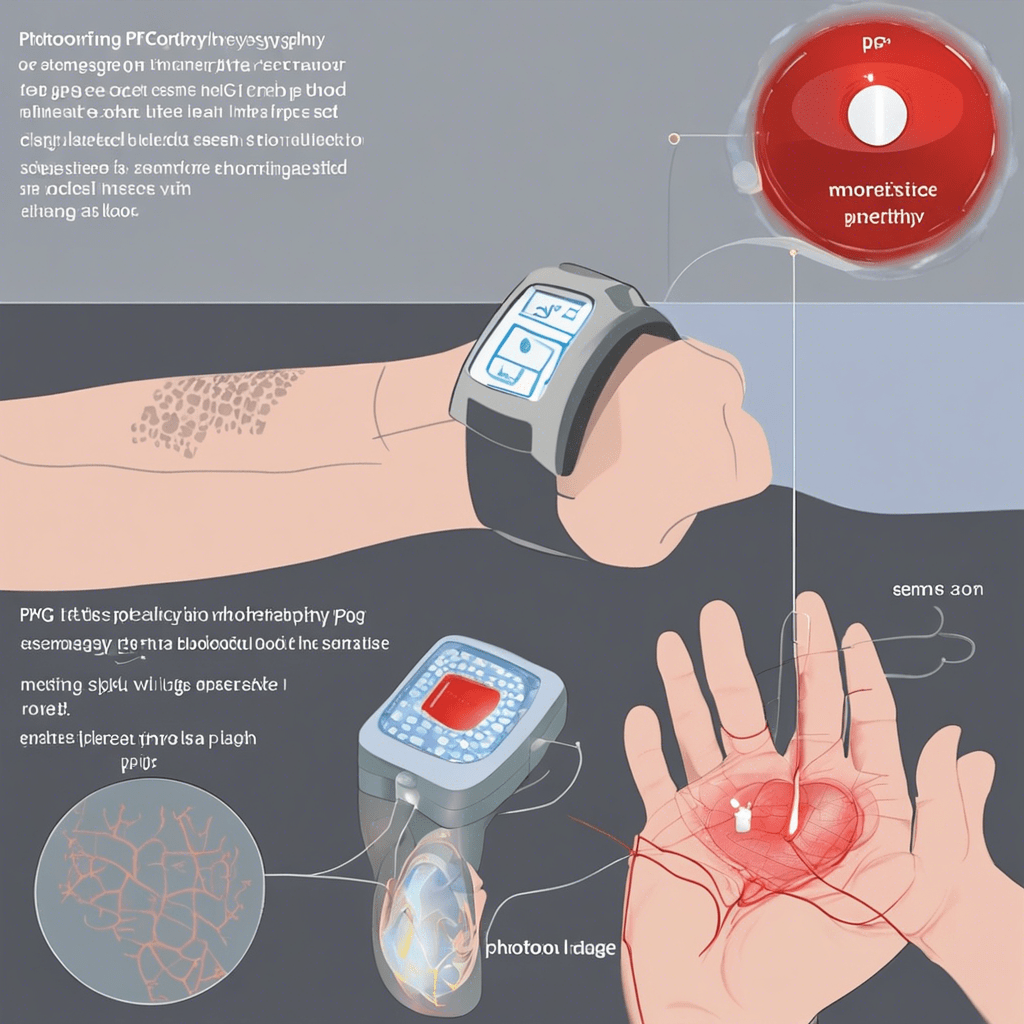
Core Components
1. Optical / Mechanical Sensors: Key components for collecting physiological data.
2. Microcontroller (MCU): Responsible for data processing and algorithm computation.
3. Display Screen: Typically an OLED or LCD screen that provides the user interface and presents real-time data.
4. Battery and Charging Module: Supplies power to the device; commonly uses lithium batteries.
5. Wireless Connectivity Module: Such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for data synchronization and communication.
6. Air Bladder Component (if applicable): Used to simulate the cuff inflation and deflation process in traditional blood pressure readings.
Current User Pain Points
1. Measurement Accuracy: Existing technology may not accurately measure blood pressure in certain scenarios, such as during physical activity or for users with hypertension, compared to traditional devices.
2. Wearing Comfort: The design of some models may cause discomfort during prolonged use, especially those with air bladder structures.
3. Data Privacy and Security: There are concerns among users about the potential for health data privacy breaches and security issues during data transmission and storage.
4. Battery Life: Frequent monitoring can lead to rapid battery depletion, which has become a significant concern for users.
Future Technology Trends
1. Higher Measurement Accuracy: With ongoing advancements in sensors and algorithms, future blood pressure smartwatches are expected to achieve higher accuracy, potentially surpassing traditional devices.
2. Multi-Functional Health Integration: More health monitoring functions, such as blood glucose and blood oxygen monitoring, may be incorporated into the smartwatch, creating a more comprehensive health management device.
3. AI and Big Data Analytics: The use of artificial intelligence and big data analysis could provide personalized health recommendations and accurately predict health risks.
4. Improved Interconnectivity: IoT technology may enable seamless integration with other health devices and smart home systems, forming a complete health ecosystem.
5. AR and VR Applications: The introduction of AR&VR could help users better understand health data through immersive experiences for health education and management.
In summary, blood pressure smartwatches are gradually transforming how people understand and approach blood pressure management. Despite current challenges, advancements in technology are expected to address these issues, making blood pressure smartwatches essential tools for comprehensive health management in the future.
留下评论